UK : 63, St Mary Axe, London, United Kingdom, EC3A 8AA
AU : Suite 202, 234 George Street, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. 2000
Email Us Mon-Fri, 10:00 AM to 6:00 PMChina’s Stimulus Efforts : Transforming Real Estate and Financial Markets

China’s economy is currently facing significant challenges. The economic slowdown is part of a broader cyclical trend, further complicated by geopolitical tensions. As the country works to implement effective recovery measures, global observers are paying close attention.
Recently, China introduced a series of stimulus initiatives aimed at revitalising its economic landscape, particularly its real estate and banking sectors. With declining property sales and increasing pressures on financial institutions, the government’s strategic interventions have captured the attention of market observers and investors alike.
These measures come on the heels of a substantial rate cut by the U.S. Federal Reserve that has given the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) more flexibility to ease its monetary conditions without exerting excessive pressure on the yuan. This synchrony in policy adjustments underscores a global trend where central banks are pivoting towards supportive measures in response to economic uncertainties.
PBOC Cuts Rates to Stimulate Growth
Following the COVID-19 outbreak in December 2019, the Chinese economy’s typical growth rate of 6% plummeted to 2.2% in 2020. The unprecedented pandemic severely impacted consumer demand, production, investment, and international trade. In 2021, growth rebounded to 8.4%, albeit from a notably low base in 2020. However, in 2022, the resurgence of COVID-19 and the implementation of strict “Zero-COVID” policies caused growth to fall back into the 3% range.
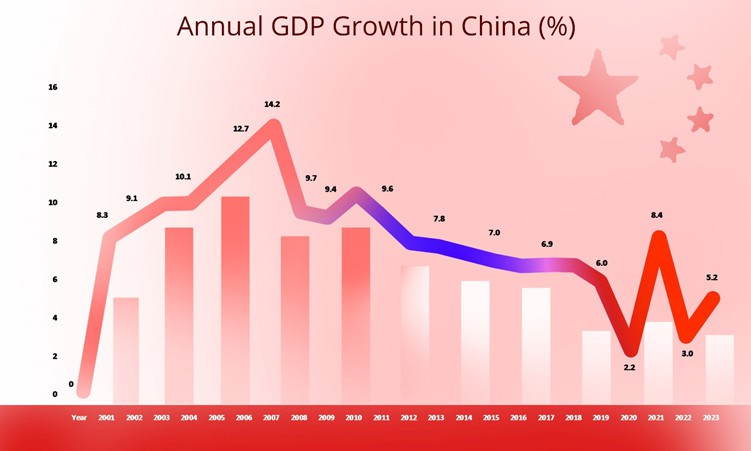
Data source: World Bank, Image Source: © 2024 Krish Capital Pty.Ltd; Analysis: Haanuwise
The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) has announced a range of measures designed to bolster economic activity, including lowering interest rates to make borrowing more affordable for consumers and businesses. This includes significant mortgage rate reductions benefiting approximately 50 million households. Additionally, the reserve requirement ratio (RRR) for banks has been cut, releasing approximately 1 trillion YUAN (US$140 billion) into the financial system to stimulate lending and investment.
Additionally, the Central Bank has allocated 200 Billion YUAN (US$28 Billion) specifically for local government investment projects, aimed at stimulating infrastructure development and providing a much-needed boost to local economies. The combined impact of these measures represents the most significant stimulus since the pandemic, a clear indication of the urgency with which the government is seeking to address economic stagnation.
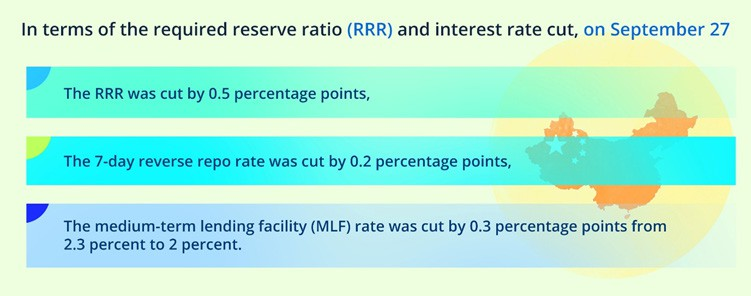
Data source: The People’s Bank of China, Image Source: © 2024 Krish Capital Pty.Ltd; Analysis: Haanuwise
Market expectations suggest that the PBOC may further cut the RRR by 0.25-0.5 percentage points, depending on the market liquidity before the year-end. In September, markets responded positively to the stimulus package, rallying to their highest levels in two years. PBOC Governor Pan Gongsheng outlined plans for lowering borrowing costs and injecting additional funds into the economy, specifically targeting households burdened by mortgage repayments. His remarks indicated potential further reductions in reserve requirements, depending on market conditions later this year. Reports also suggest that Beijing may also introduce 2 Trillion YUAN (US$284 Billion) in sovereign bonds, aimed at addressing local government debt and enhancing the social safety net.
According to the World Bank, China’s GDP growth is anticipated to be 4.8 percent in 2024, which is an increase of 0.3 percentage points from the December 2023 estimate. This adjustment is attributed to stronger-than-expected exports, as well as the effects of policy initiatives aimed at supporting the property market and increased fiscal spending.
Boosting Real Estate Stability in China
The data for real estate development and sales in China from January to September 2024 shows a general decline in investment compared to the previous year and highlights a downturn in real estate investment across all sectors, particularly in residential and commercial developments.
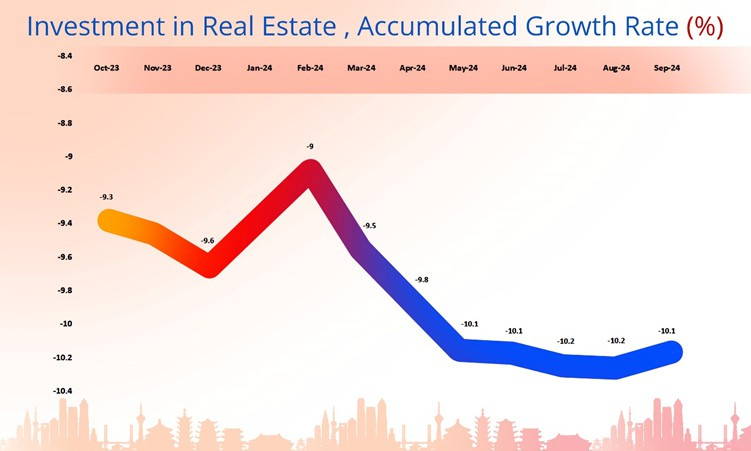
Data source: National Bureau of Statistics of China Image Source: © 2024 Krish Capital Pty.Ltd; Analysis: Haanuwise
Moreover, data from the past 10 years reflect that investment in real estate development peaked in 2021 and then started following a downward trend.
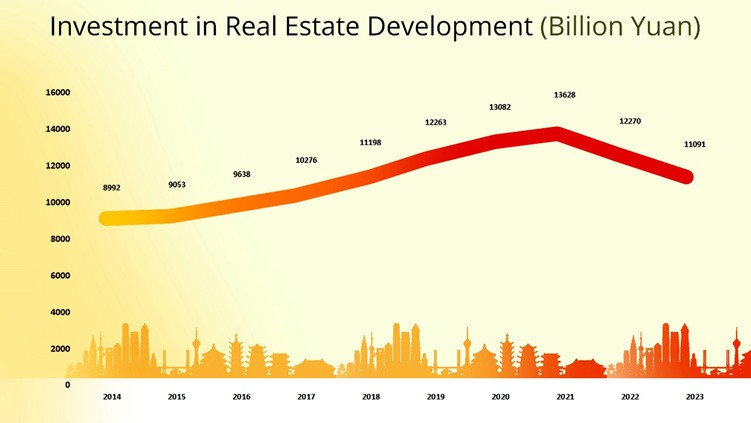
Data source: National Bureau of Statistics of China, Image Source: © 2024 Krish Capital Pty.Ltd; Analysis: Haanuwise
China has been implementing a series of policies aimed at rejuvenating its residential sales market and promoting the healthy development of the real estate sector. Key initiatives include easing restrictions for first-home buyers, lowering existing mortgage rates, and extending tax incentives for property purchases. These measures are designed to enhance accessibility for prospective homeowners and stimulate market activity. China’s major national commercial banks have begun implementing mortgage rate adjustment plans, aiming to boost confidence in the property sector, which is gaining momentum.
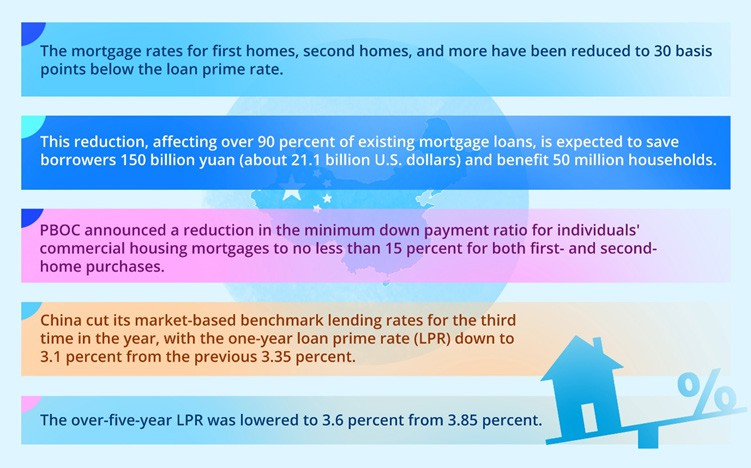
Data source: https://english.www.gov.cn/ The State Council The People’s Republic of China, Image Source: © 2024 Krish Capital Pty.Ltd; Analysis: Haanuwise
Recent government meetings have highlighted significant shifts in the supply-demand dynamics within the real estate market. The pro-housing policies introduced in September have already led to “positive changes in the real estate market.” By October 16, loans approved for “whitelist” real estate projects had reached 2.23 Trillion Yuan (approximately 313 Billion U.S. dollars). Experts predict that this amount will exceed 4 trillion yuan by the end of the year. To further alleviate the financial burden on homeowners, China’s Central Bank has urged commercial banks to lower interest rates on existing mortgage loans, a move expected to save borrowers around 150 Billion Yuan.
While these initiatives may temporarily boost market confidence, they could also exert pressure on banks’ net interest margins due to reduced borrowing rates. As the economy adjusts, it is vital to focus on sustainable growth strategies that extend beyond immediate relief. Long-term stability will depend on balanced policies that address structural issues and rebuild investor trust in the property market.
Disclaimer – The information available on this website is provided for education and informational purposes only. It does not constitute or provide financial, investment or trading advice and should not be construed as an endorsement of any specific stock or financial strategy in any form or manner. We do not make any representations or warranties regarding the quality, reliability, or accuracy of the information provided. This website may contain links to third-party content. We are not responsible for the content or accuracy of these external sources and do not endorse or verify the information provided by third parties. We are not liable for any decisions made or actions taken based on the information provided on this website.




